16.10.2008
Mars Express Phobos Observation Series
Between 23rd July and 15th September 2008 the Mars Express spacecraft made a series of eight flybys of the inner moon of Mars, Phobos, at distances ranging from 4500 km down to 93 km from the centre of the moon. The irregular 27 km × 22 km × 19 km body was imaged at each pass by both the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) and the Super Resolution Channel (SRC).
|
|
Animation of Phobos shape model 
|
Animation of Phobos shape model (spherical harmonic function of degree and order 17) based on control point network derived from 53 SRC and 16 Viking images. The model is draped with a mosaic of the same images, the SRC coverage being over 70% of the moon´s surface. Mean resolution: 12 m/pixel
Credits: ESA/ DLR (K.Willner)/ FU Berlin (G. Neukum)
|
[Download Animation] (with Rightclick and "Save as...")
|
In observing Phobos, Mars Express benefits from its highly elliptical orbit which takes it from a closest Mars approach of 270 km above the surface up to a maximum of 10 000 km distant from the planet´s centre, crossing the 9 400 km orbit of the moon. Like our Moon, Phobos always shows the same side to the planet, so it is only by flying outside the orbit that it becomes possible to observe the far side. The other spacecraft presently orbiting Mars do so at much lower altitudes, and therefore only see the planet-facing side of the moon.
After the highest resolution coverage acquired during the 93 km approach (previously released images), on 26th July in orbit 5861 Phobos was imaged with all nine channels of HRSC. HRSC is a so-called push-broom camera, which builds up the images a line at a time as the spacecraft passes over the surface. It has nine scanning lines (or channels), oriented in directions spread from 18.9° behind nadir (vertical), to 18.9° ahead of nadir, which give the camera its stereo-viewing capacity. Four of the lines have colour filters: these are interspersed between five panchromatic lines. The image channel sequence from this observation gives a striking impression of the fleeting encounter (figure 2). The flyby of orbit 5984 on 30th August produced the data for the first HRSC colour image of Phobos (figure 1). It was known that the colour of the moon is highly uniform: nevertheless, some subtle variations can be seen.
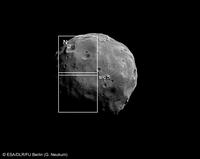
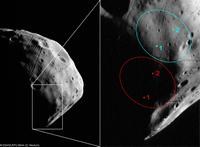
In 2009, the Russian Federal Space Agency will send a mission called Phobos Grunt (meaning Phobos Soil) to land on the Martian moon, collect a soil sample, and return it to Earth for analysis. For operational reasons, a landing site was selected on the side facing away from Mars, a place last seen in the 1970s by the Viking orbiters. These Mars Express observations have been much awaited to better assess the selection and more deeply characterise the site, and already as a consequence it is being considered to move the position slightly to the north, to a safer area between 7°-21°S and 214°-233°W.
The Super Resolution Channel (SRC), a part of the HRSC experiment, is an additional camera sharing the same processing electronics. Unlike HRSC, SRC is a framing camera, taking a complete image during a single exposure like a conventional pocket camera. It uses a 975 mm Maksutov-Cassegrain telescope, which gives it a nominal pixel-resolution about four times higher than that of HRSC; by September 2008 it had captured over 6000 images. Early in the mission, the thermal conditions of the instrument in space caused a distortion in its precision optics, resulting in a lesser performance than expected: some blur and ghosting is seen in the raw images. However, by analysing the effect of the distortion on point-like star images and applying corrective processing, it has been possible to reverse a significant part of the degradation (figure 3 and figure 4). During close flybys, when the relative speed of the spacecraft passing the moon is around 3 km/s, it was known there would also be some motion smear in the images. Work continues in the HRSC group at the Freie Universitaet in Berlin to remove these combined effects.
The origin of Phobos is debated: it appears to share many surface characteristics with the class of carbonaceous C-type asteroids, which suggests it might have been captured from this population. However, it is difficult to explain either the capture mechanism or the subsequent evolution of the orbit into the equatorial plane of Mars. An alternative hypothesis is that it formed in its present position, and is therefore a remnant from the planetary formation period.
During the flybys, it was possible to detect the gravitational influence of the moon on the trajectory of Mars Express allowing a precise determination of the moon's mass. HRSC's stereo observations and tie-point measurements between SRC images allow us to produce a 3-D model of the body (see the animation on top). This, together with the mass, will provide a precise value for the mean density of Phobos, telling us much about the compositional possibilities: how much rock or ice may be present, and how porous the structure may be - perhaps tipping the balance for the origin debate one way or the other.
| Date | Orbit | Mean Anomaly | Distance in km | HRSC channels | Best nadir resolution in m/pixel | SRC images | Nominal SRC resolution in m/pixel |
| 23/07/2008 | 5850 | 3,58 | 4478 | nd | 180 | 8 | 41 |
| 23/07/2008 | 5851 | 342,48 | 93 | nd, s1, s2, p1, p2 | 3.7 | 4 | 0.8 |
| 26/07/2008 | 5861 | 333,33 | 2295 | nd, s1, s2, p1, p2, bl, re, gr, ir | 90 | 8 | 20 |
| 28/07/2008 | 5870 | 339,65 | 351 | nd, s1, s2, p1, p2 | 14 | 8 | 3.2 |
| 03/08/2008 | 5889 | 337,13 | 656 | nd, s1, s2, bl, re, gr, ir | 26 | 8 | 6 |
| 08/08/2008 | 5908 | 334,5 | 1024 | bl, re, gr, ir | 41 | 8 | 9.3 |
| 30/08/2008 | 5984 | 325,02 | 2366 | nd, s1, s2, bl, re, gr, ir | 95 | 8 | 22 |
SRC Images
Download
hochaufgelöste Bilddaten / high resolution image data
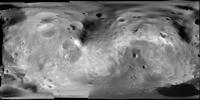
Phobos SRC mosaic derived from 53 SRC images, covering over 70% of the moon's surface. The remaining area is filled with 16 Viking images. Mean resolution: 12 m/pixel
Credits: ESA/ DLR (S. Semm, M. Wählisch, K.Willner)/ FU Berlin (G. Neukum): | TIF
(16 MBs) | JPG
(896 KBs) | |
| HRSC orbit 5851 stereo-1 channel. Resolution: 3.7 m/pixel. The ellipses show the previously (red) and currently (blue) considered landing sites for the Phobos Grunt spacecraft. The change was made on the basis of this image series.: | TIF
(6 MBs) | JPG
(606 KBs) | |
| Phobos nadir-channel image: This image has additionally been enhanced photometrically for better bringing features in the less illuminated part.: | TIF
(4 MBs) | JPG
(1 MB) | |
| HRSC orbit 5889 nadir channel with SRC footprints. Resolution: 26 m/pixel: | TIF
(526 KBs) | JPG
(120 KBs) | |
| HRSC orbit 5889 nadir channel. Resolution: 26 m/pixel: | TIF
(524 KBs) | JPG
(115 KBs) | |
| HRSC orbit 5870 nadir channel with SRC footprints. Resolution: 14 m/pixel: | TIF
(1 MB) | JPG
(338 KBs) | |
| HRSC orbit 5870 nadir channel. Resolution: 14 m/pixel: | TIF
(1 MB) | JPG
(329 KBs) | |
| HRSC three-channel sequence, orbit 5870. Resolution: 14 m/pixel.: | TIF
(1 MB) | JPG
(238 KBs) | |
| Figure 2: HRSC nine-channel sequence, orbit 5861. Note that four channels, IR - infra-red, GR - green, BL - blue, and RE - red, are taken through colour filters and so have a different appearance. Original channels recorded at resolution from 92-470 m/pixel; here all shown at 92 m/pixel.: | TIF
(263 KBs) | JPG
(78 KBs) | |
| Figure 3: Orbit 5889: raw SRC image 2, SRC image 2 corrected for mirror distortion, and portion of HRSC nadir showing same region. The corrected SRC image shows significantly more detail than the HRSC nadir image. Resolution: 3.2 m/pixel (SRC), 14 m/pixel (HRSC): | TIF
(3 MBs) | JPG
(256 KBs) | |
| Figure 4: SRC orbit 5984 image 5, before and after correction for mirror distortion. Resolution: 22 m/pixel: | TIF
(1005 KBs) | JPG
(141 KBs) | |
| HRSC orbit 5908 green channel with SRC footprints. Resolution: 41 m/pixel: | TIF
(247 KBs) | JPG
(60 KBs) | |
| HRSC orbit 5908 green channel. Resolution: 41 m/pixel: | TIF
(247 KBs) | JPG
(56 KBs) | |
| Figure 1: HRSC orbit 5984 colour image. Pan-sharpened composite of nadir, green and blue channels. The differing viewing geometry between channels was eliminated by registering over tie-points. Resolution: 95 m/pixel: | TIF
(162 KBs) | JPG
(12 KBs) | |
| HRSC Stereo anaglyph: orbit 5870, stereo-1 and photometry-1 channels. Resolution: 15 m/pixel.: | TIF
(3 MBs) | JPG
(294 KBs) | |
| HRSC Stereo anaglyph: orbit 5870, stereo-2 and photometry-2 channels. Resolution: 15 m/pixel.: | TIF
(4 MBs) | JPG
(282 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5861 image 5, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 20 m/pixel: | TIF
(1 MB) | JPG
(103 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5870 image 2, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 3.2 m/pixel: | TIF
(465 KBs) | JPG
(79 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5870 image 3, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 3.2 m/pixel: | TIF
(489 KBs) | JPG
(83 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5870 image 4, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 3.2 m/pixel: | TIF
(505 KBs) | JPG
(87 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5870 image 5, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 3.2 m/pixel: | TIF
(534 KBs) | JPG
(95 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5889 image 2, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 6 m/pixel: | TIF
(294 KBs) | JPG
(49 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5889 image 3, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 6 m/pixel: | TIF
(1 MB) | JPG
(94 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5889 image 4, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 6 m/pixel: | TIF
(1 MB) | JPG
(95 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5889 image 5, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 6 m/pixel: | TIF
(1 MB) | JPG
(57 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5908 image 4, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 9 m/pixel: | TIF
(513 KBs) | JPG
(90 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5908 image 5, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 9 m/pixel: | TIF
(396 KBs) | JPG
(72 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5984 image 4, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 22 m/pixel: | TIF
(336 KBs) | JPG
(62 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 5984 image 5, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 22 m/pixel: | TIF
(1 MB) | JPG
(70 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 6042 image 4, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 34 m/pixel: | TIF
(242 KBs) | JPG
(52 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 6042 image 5, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 34 m/pixel: | TIF
(1 MB) | JPG
(54 KBs) | |
| SRC orbit 6042 image 6, corrected for mirror distortion. Resolution: 34 m/pixel: | TIF
(1023 KBs) | JPG
(40 KBs) | |
© Copyright: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin (G. Neukum)


 Deutsch
Deutsch